Constructing Complex Shapes with Signed Distance Functions: The Heart Example
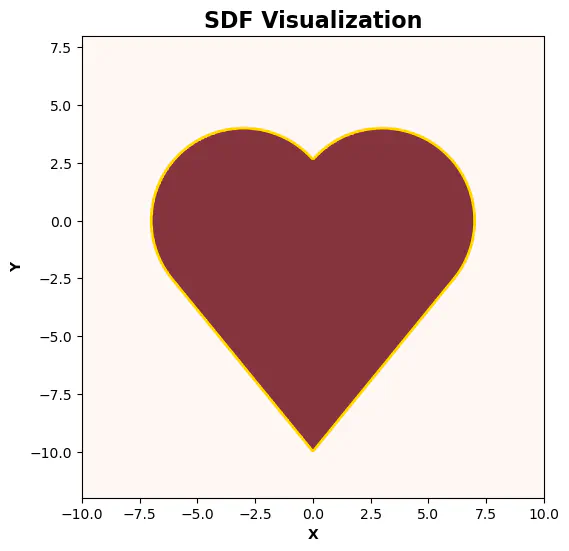 Signed Distance Function (SDF) of the Heart Shape
Signed Distance Function (SDF) of the Heart ShapeIn this notebook, we’ll implement a signed distance function for a heart shape using Python and visualize it using matplotlib.
Function Definitions
The following functions are defined:
line_sdf: Calculates the signed distance from a point to a line segment.circle_sdf: Calculates the signed distance from a point to a circle.intersect_sdf: Calculates the signed distance field resulting from the intersection of two distance fields.union_sdf: Calculates the signed distance field resulting from the union of two distance fields.
1import numpy as np
2import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3
4def line_sdf(P, x1, y1, x2, y2):
5 """
6 Calculate the signed distance from a point P to a line segment
7 defined by two endpoints (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
8 """
9
10 a = np.array([x2 - x1, y2 - y1])
11 a = a / np.linalg.norm(a)
12 b = P - np.array([x1, y1])
13 d = np.dot(b, np.array([a[1], -a[0]]))
14 return d
15
16def circle_sdf(P, xc, yc, r):
17 """
18 Calculate the signed distance from a point P to a circle defined by its center (xc, yc) and radius r.
19 """
20 return np.sqrt((P[0] - xc) ** 2 + (P[1] - yc) ** 2) - r
21
22def intersect_sdf(d1, d2):
23 """
24 Calculate the signed distance field resulting from the intersection of two distance fields (d1 and d2).
25 """
26 return max(d1, d2)
27
28def union_sdf(d1, d2):
29 """
30 Calculate the signed distance field resulting from the union of two distance fields (d1 and d2).
31 """
32 return min(d1, d2)
Tangent Point Calculation
The find_tangent_point function finds the tangent point that has a specified distance from the bottom tip of the heart shape. This function is inspired by this post and this gist.
1def find_tangent_point(x1, y1, d1, x2, y2, d2):
2 """
3 Find the tangent point that has radius(d1) distance from center of circle
4 and calculated distance (d2) from the bottom tip of the heart. The result is
5 limited to desired tangent point.
6 """
7
8 centerdx = x1 - x2
9 centerdy = y1 - y2
10 R = np.sqrt(centerdx**2 + centerdy**2)
11
12 if not (abs(d1 - d2) <= R and R <= d1 + d2):
13 # No intersections
14 return []
15
16 d1d2 = d1**2 - d2**2
17 a = d1d2 / (2 * R**2)
18
19 c = np.sqrt(2 * (d1**2 + d2**2) / R**2 - (d1d2**2) / R**4 - 1)
20
21 fx = (x1 + x2) / 2 + a * (x2 - x1)
22 gx = c * (y2 - y1) / 2
23 # ix1 = fx + gx
24 ix2 = fx - gx
25
26 fy = (y1 + y2) / 2 + a * (y2 - y1)
27 gy = c * (x1 - x2) / 2
28 # iy1 = fy + gy
29 iy2 = fy - gy
30
31 return [ix2, iy2]
Heart Shape SDF
The heart_sdf function calculates the signed distance from a point to a heart shape defined by two circles and three line segments.
1def heart_sdf(p, r=4):
2 """
3 Calculate the signed distance from a point P to a heart shape defined by two circles and three line segments.
4
5 The heart shape consists of two circles representing the left and right sides, and three line segments representing the bottom tip and the tangent lines connecting the circles.
6
7 Parameters:
8 p (tuple): A tuple containing the coordinates (x, y) of the point P.
9 r (float): The radius of the heart shape. Default is 4.
10
11 Returns:
12 float: The signed distance from the point P to the heart shape. Negative values indicate that the point is inside the heart shape, zero indicates that the point is on the boundary, and positive values indicate that the point is outside the heart shape.
13
14 Note:
15 The heart shape is constructed based on mathematical equations and geometric calculations. The function utilizes signed distance functions (SDFs) for circles and lines to determine the distance from the point P to various components of the heart shape.
16 """
17 # Some experimental ratio for the center of circles based on their radius
18 a = r * 3 / 4
19
20 circle1 = circle_sdf(p, -a, 0, r) # Left Circle
21 circle2 = circle_sdf(p, a, 0, r) # Right Circle
22
23 # Distance from bottom tip to center of circles
24 d2c = np.sqrt((a - 0) ** 2 + (0 - 2 * a - r) ** 2)
25
26 # Distance to tangent point of circle using Pythagorean theorem
27 d2t = np.sqrt(d2c**2 - r**2)
28
29 tpr = find_tangent_point(
30 a, 0, r, 0, -2 * a - r, d2t
31 ) # Tangent point on right circle
32
33 line1 = line_sdf(p, -tpr[0], tpr[1], 0, -2 * a - r)
34 line2 = line_sdf(p, 0, -2 * a - r, tpr[0], tpr[1])
35 line3 = line_sdf(p, tpr[0], tpr[1], -tpr[0], tpr[1])
36
37 # Create a triangle which base is the line that
38 # connects tangent points and the vertex point is heart bottom tip
39
40 dl = intersect_sdf(intersect_sdf(line1, line2), line3)
41
42 d = union_sdf(union_sdf(circle1, circle2), dl)
43
44 return d
Visualization
The plot_sdf function plots the signed distance function. This function is adopted from pyPolyMesher project.
1def plot_sdf(SDF, BdBox=[-10, 10, -12, 8], n=300):
2 """
3 Plots the signed distance function.
4 """
5 x, y = np.meshgrid(
6 np.linspace(BdBox[0], BdBox[1], n),
7 np.linspace(BdBox[2], BdBox[3], n),
8 )
9 points = np.hstack([x.reshape((-1, 1)), y.reshape((-1, 1))])
10
11 sdf = np.fromiter(map(SDF, points), dtype=float)
12
13 inner = np.where(sdf <= 0, 1, 0)
14
15 _, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
16 _ = ax.imshow(
17 inner.reshape((n, n)),
18 extent=(BdBox[0], BdBox[1], BdBox[2], BdBox[3]),
19 origin="lower",
20 cmap="Reds",
21 alpha=0.8,
22 )
23 ax.contour(x, y, sdf.reshape((n, n)), levels=[0], colors="gold", linewidths=2)
24 ax.set_xlabel("X", fontweight="bold")
25 ax.set_ylabel("Y", fontweight="bold")
26 ax.set_title("SDF Visualization", fontweight="bold", fontsize=16)
27 ax.set_aspect("equal")
28
29 plt.show()
Now let’s execute the plot_sdf function to visualize the signed distance function for the heart shape.
1plot_sdf(heart_sdf)
The full code, ready to copy and try, is also available at this gist.